Introduction
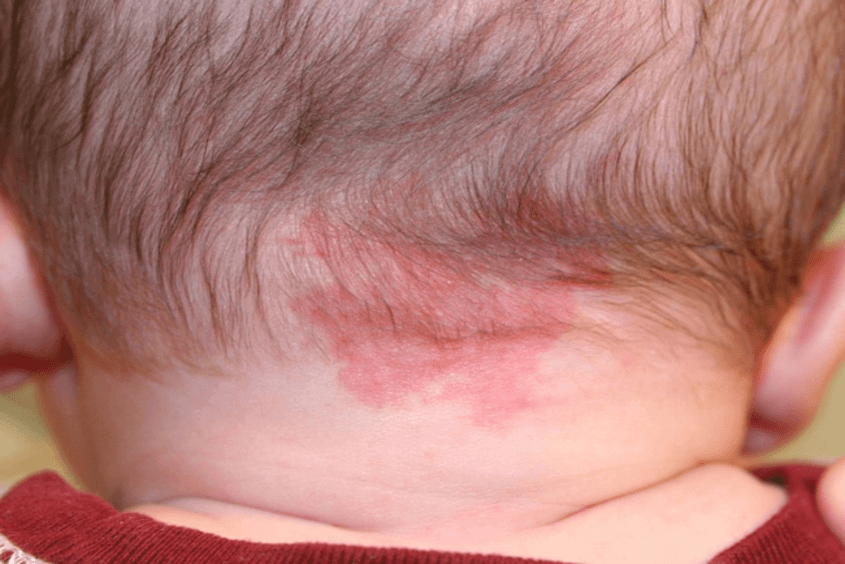
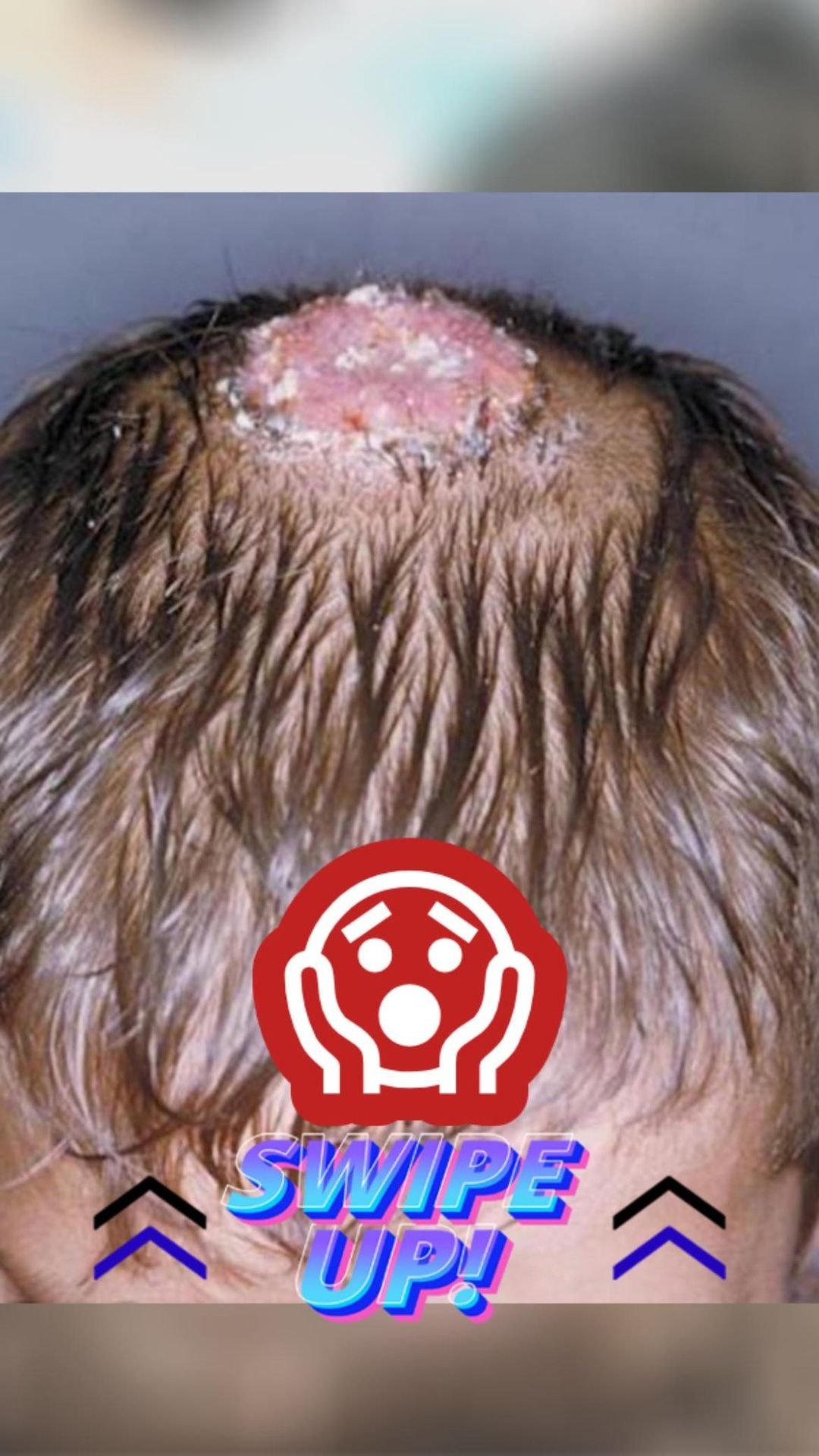
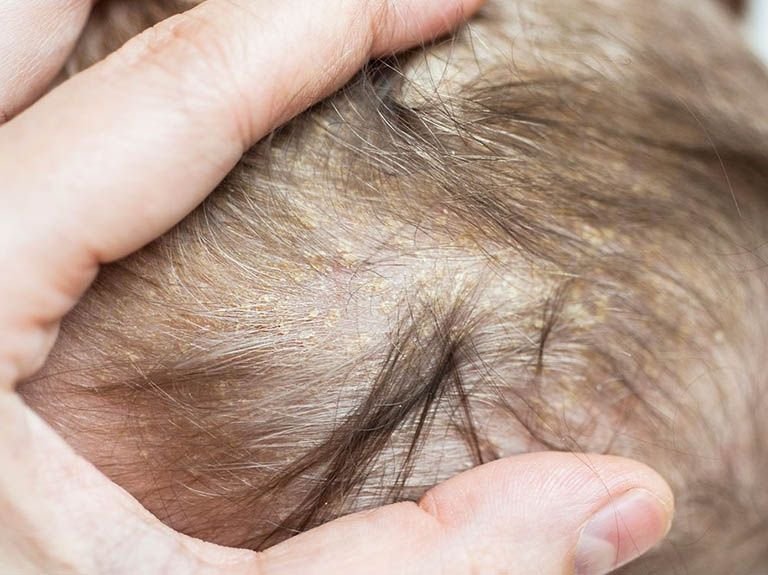
Scalp fungal infections, known medically as tinea capitis, are a significant health issue in children. Initially appearing as minor irritations, these infections can escalate into serious complications without timely and effective intervention. This guide delves into the possible repercussions of scalp fungal infections in young individuals, offering essential insights for parents.
Spread of Infection A primary concern with scalp fungal infections is their potential to spread rapidly. The fungi that cause these conditions flourish in the warm, moist environments of a child’s scalp. Without appropriate treatment, the infection can extend to other parts of the body or be transmitted to peers through direct contact, underscoring the urgency of managing these infections properly.
Secondary Bacterial Infections The itchiness of scalp fungal infections often leads children to scratch the affected areas, which can compromise the skin’s integrity and allow bacteria to enter, leading to secondary bacterial infections. These complications necessitate a more extensive treatment strategy, highlighting the importance of managing the initial fungal issue promptly.
Permanent Hair Loss In severe scenarios, neglected or improperly treated fungal infections can cause permanent hair loss. The fungi damage the hair follicles, potentially leading to lasting scarring and hair loss. This severe outcome underscores the critical need for early detection and correct medical treatment.
Psychosocial Impact The physical symptoms of scalp fungal infections, such as redness, scaling, and hair loss, can also inflict significant emotional and social stress on children, leading to embarrassment and a diminished sense of self-esteem. Prompt treatment of these infections is vital not only for physical health but also for the emotional well-being of the affected child.
Chronic Infections Sometimes, scalp fungal infections may persist or recur despite initial treatment efforts, suggesting a possible resistance to standard antifungal medications or an incomplete eradication of the fungus. Persistent infections necessitate a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals to devise an effective treatment plan.
Family and Community Concerns Given the high contagiosity of scalp fungal infections, it is crucial for parents to prevent the spread within the home and community. Close interactions among children and family members facilitate the transmission of the infection. Educating everyone in the household and immediate community on maintaining proper hygiene is essential in controlling the spread of the infection.
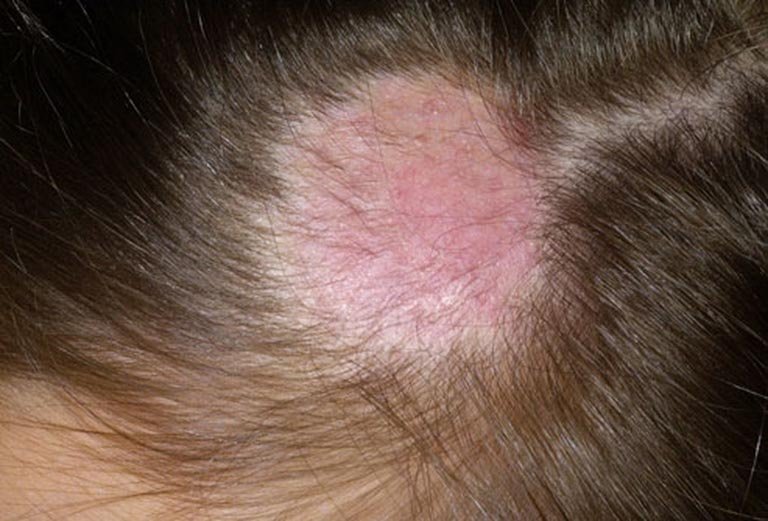
Conclusion Scalp fungal infections in children, while common, can lead to significant complications if not addressed with urgency and effectiveness. Parents must prioritize early detection, appropriate treatment, and preventative measures to mitigate the impact on their child’s health and social life. Should a scalp fungal infection be suspected, immediate medical consultation is imperative to ensure a swift and effective resolution.