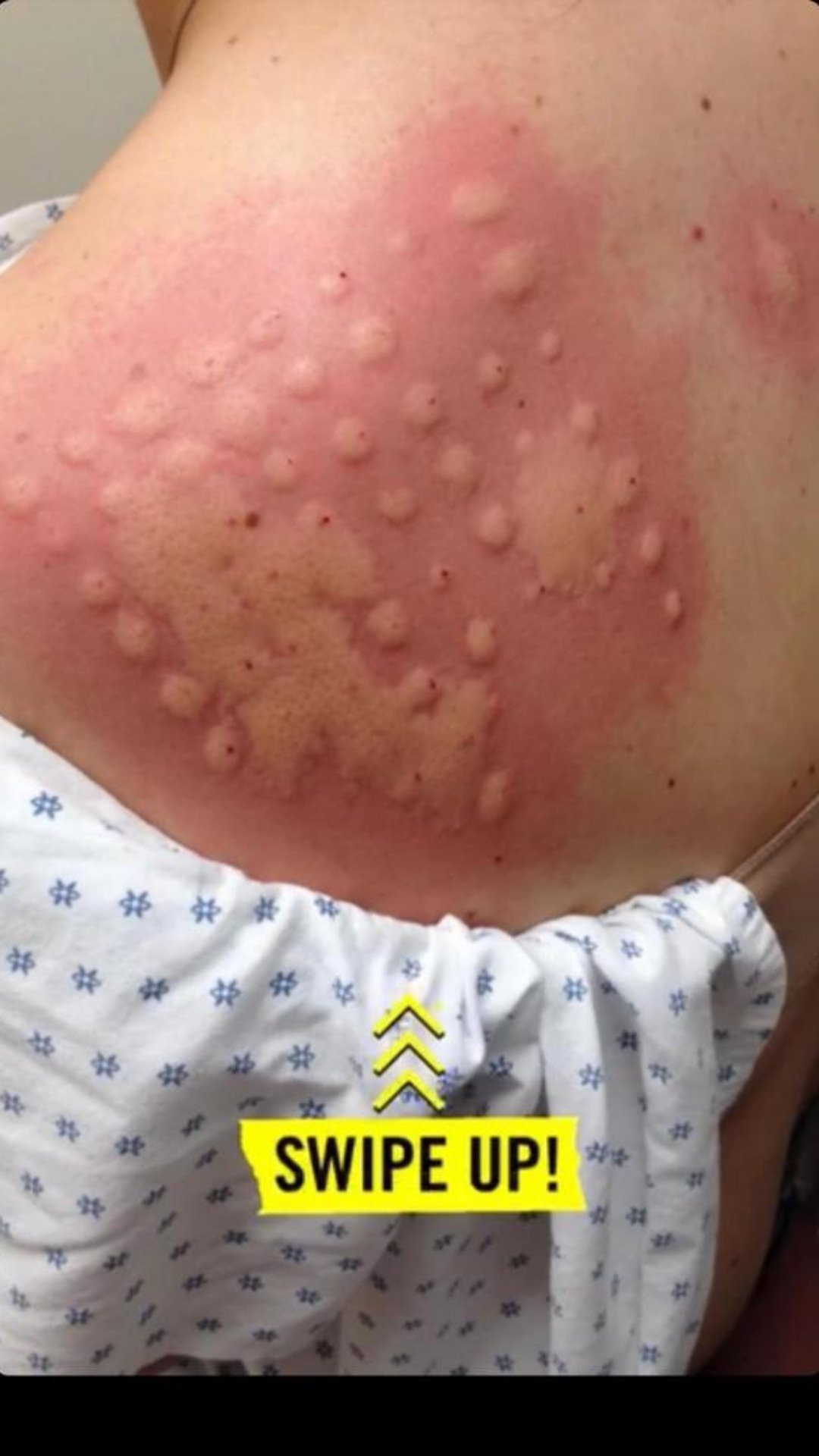
Itchy back is a common problem caused by various factors. It can be a nuisance, disrupting sleep and concentration. In some cases, it might indicate a more serious medical condition.
This article discusses the causes, symptoms, and treatments of an itchy back, along with preventive tips.
If you are experiencing an itchy back, it’s important to consult a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.

Causes
There are many causes of an itchy back. Some of the most common include:
Dry Skin: Dry skin often leads to itching, particularly on the back. Contributing factors include:
- Lack of Hydration: Not drinking enough water can result in dry skin.
- Excessive Bathing: Frequent bathing can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness.
- Hot Weather: Hot weather can also dry out the skin.
Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions to certain substances, such as specific foods, medications, or environmental irritants, can also cause itching.
Infections: Skin infections, such as fungal or bacterial infections, can cause itching.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, like eczema, psoriasis, or liver disease, can also cause itching.
Problems
In addition to itching, a person with an itchy back may experience other symptoms, such as:
- Rash: A rash may appear on the back, and it may be red, swollen, or bumpy.
- Scales: Scales may appear on the back, and they may be dry, flaky, or crusty.
- Crusting: Crusting may appear on the back, and it may be thick or thin.
- Bleeding: Bleeding may occur if the skin is scratched.
Prevention
Several measures can help prevent an itchy back, including:
- Drink Plenty of Fluids: Staying hydrated helps keep the skin moisturized.
- Take Short, Cool Baths or Showers: Avoiding long, hot baths helps preserve the skin’s natural oils.
- Use a Mild Soap: Mild soap helps avoid drying out the skin.
- Apply Moisturizer to the Back: Regular moisturizing keeps the skin hydrated.
- Avoid Scratching: Scratching can worsen itching and lead to skin damage.

Treatment
The treatment for an itchy back depends on the underlying cause. If dry skin is the cause, moisturizing the back will help. For allergic reactions, avoiding the allergen will relieve itching. Infections may require antibiotics or antifungal medications. Treating any underlying medical condition will also help relieve itching.
In some cases, a doctor may prescribe medication to help relieve the itching.
Additional tips for treating an itchy back include:
- Apply a Cold Compress: A cold compress can soothe the skin.
- Take Over-the-Counter Medications: Antihistamines or pain relievers can help.
- Consult a Doctor if Itching is Severe: Professional advice is essential for persistent or severe itching.
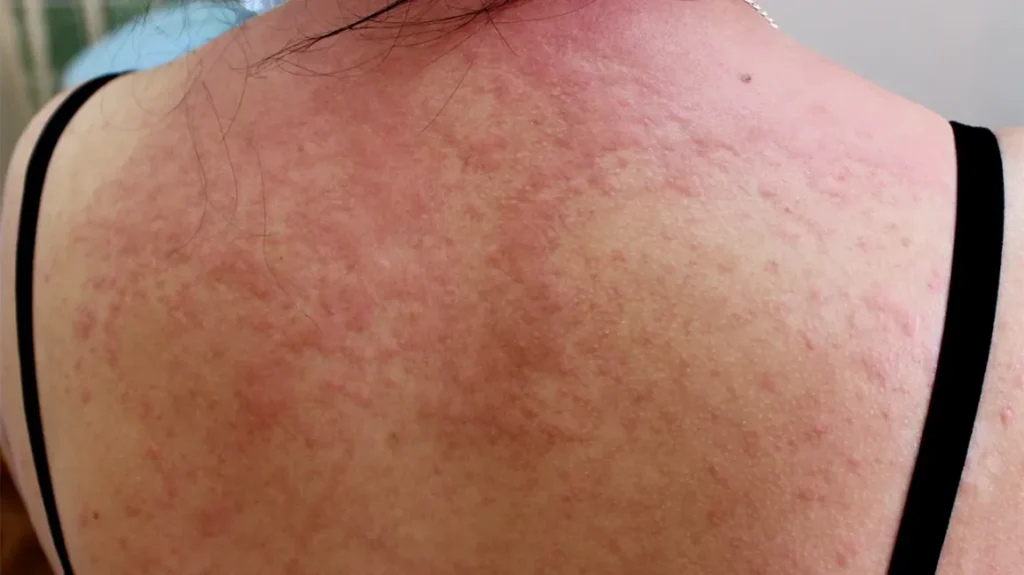
Itchy Skin: Causes and Diagnosis
Itchy skin, or pruritus, is a common skin irritation. It can occur anywhere on the body and is often very uncomfortable.

Common causes of itchy skin include:
- Dry Skin: Dry and flaky skin, often from weather changes or soap use.
- Insect Bites: Usually accompanied by a bump or blister, redness, and swelling.
- Hives: Raised, bumpy rash, often from allergies or infections.
- Heat Rash: Small pink or red spots, common in babies.
- Eczema: Red, scaly patches often found on the neck, wrists, and elbows.
- Scabies: Itchy rash caused by mites, appearing as red lumps and tracks.
- Psoriasis: Thick, scaly patches, often on the scalp, knees, and elbows.
- Obstetric Cholestasis: Rare, all-over itching during pregnancy, particularly in the last trimester.
Itchy skin can also be caused by certain medications, recreational drugs, or herbal supplements. In older adults, it may signal serious medical conditions like kidney failure, liver disease, blood disorders, thyroid issues, HIV infection, advanced cancer, or neurological conditions.

When to See a Doctor
Consult a doctor if:
- You are very itchy with no rash.
- A persistent rash doesn’t go away.
- You feel unwell or have a fever.
- Symptoms keep recurring.
- Itching prevents sleep.
- The rash is bleeding, scabbed, or has pus.
- Severe itching occurs during pregnancy.
- Your baby develops a rash.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Most causes of itchy skin can be diagnosed by a physical examination. Sometimes, additional tests like a skin biopsy, blood tests, urine tests, or stool tests may be needed.
Treatment of Itchy Skin
To alleviate itchy skin:
- Avoid Scratching: Scratching worsens the itch.
- Keep Nails Short: Prevent skin damage from scratching.
- Wear Loose Cotton Clothing: Avoid overheating and irritation from fabrics like wool.
- Reduce Stress: Techniques like meditation, yoga, and exercise can help.
- Cool Bath or Shower: Provides short-term relief.
- Avoid Harsh Soaps: Use soap-free cleansers.
- Moisturize Regularly: Apply moisturizer frequently, especially after bathing.

Prevention
To prevent itchy skin:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water.
- Use a Humidifier: Helps in dry weather.
- Quick, Cool Showers: Avoid hot water.
- Mild Soap and Moisturizer: Use after bathing while skin is damp.
Complications
Scratching can lead to a cycle of itching and scratching, causing pain, infection, marks, lumps, bruising, or scarring. If your itchy skin persists or worsens, seek medical advice.