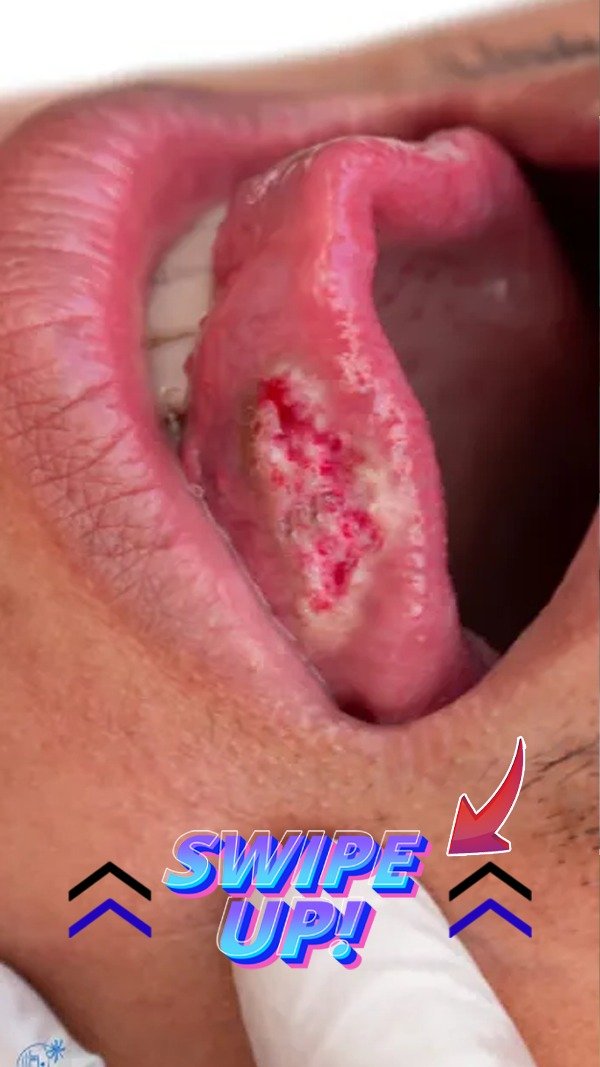
Overview
Aphthous ulcers, commonly known as canker sores, are minor yet painful lesions that form inside the mouth. These ulcers are prevalent across different age groups and typically appear as small, round, or oval lesions that are less than one centimeter in diameter, characterized by a white or gray center and a red inflamed border. They can develop on the inner surfaces of the cheeks, lips, tongue, or gums.
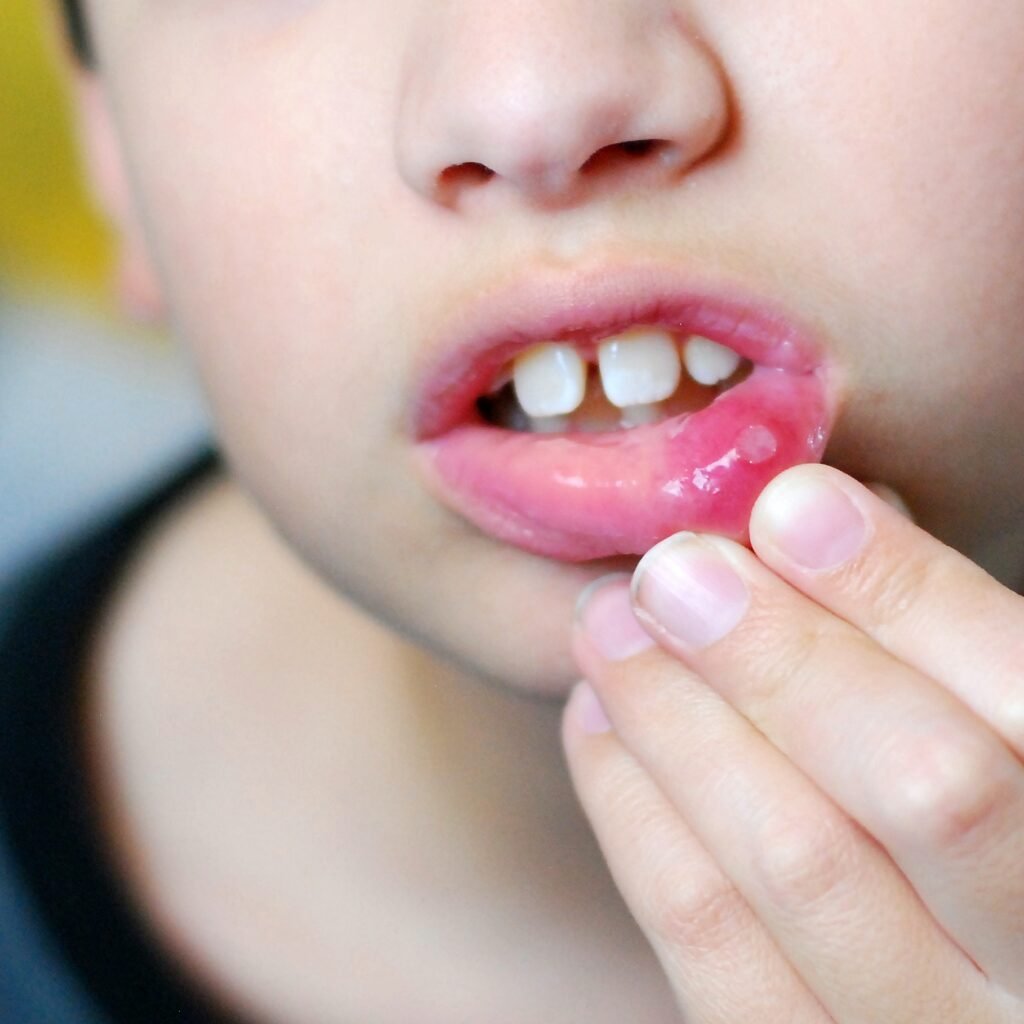
Etiology of Aphthous Ulcers
The definitive cause of aphthous ulcers remains unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to their occurrence:
- Stress: Recognized as a significant trigger for the development of these ulcers.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Insufficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, or folate can heighten the risk of these ulcers.
- Allergic Reactions: Sensitivities to specific foods or substances may initiate the onset of ulcers.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like celiac disease or Crohn’s disease are sometimes linked with aphthous ulcers.
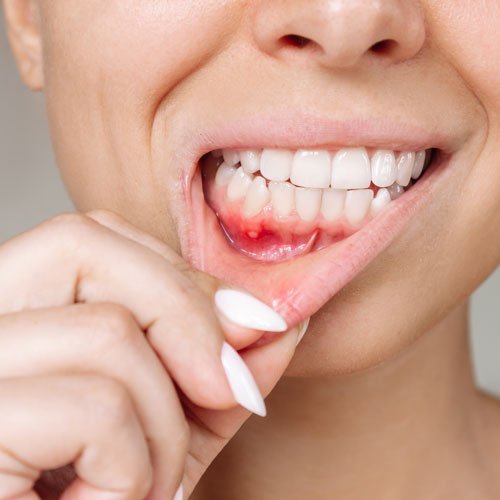
Treatment Strategies
Although aphthous ulcers generally heal independently within 10-14 days, several measures can help alleviate their discomfort:
- Dietary Considerations: Avoid acidic foods and beverages to reduce irritation to the ulcers.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Topical Applications: Medications such as benzocaine or lidocaine can provide temporary relief by numbing the area.
- Antiseptic Mouthwashes: These can help reduce bacterial growth and inflammation in the mouth.
Patients experiencing frequent or severe outbreaks should consult a healthcare provider, as prescription medications may be necessary.
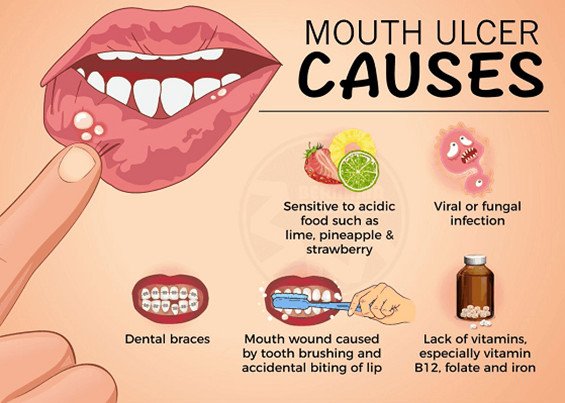
Prescription Treatments
- Corticosteroids: These medications are used to decrease inflammation and alleviate the pain associated with ulcers.
- Immunosuppressants: Useful in severe cases, these drugs help suppress the immune system to reduce ulcer formation.
- Additional Treatments: Depending on the cause, treatments may include antiviral medications for virus-induced ulcers or antibiotics for bacterial infections.
Prevention Techniques
Complete prevention of aphthous ulcers may not be possible, but the following strategies can minimize the risk:
- Nutritious Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains ensures adequate nutrient intake, bolstering the immune system.
- Stress Management: Employing stress-reduction techniques such as exercise or relaxation methods can help mitigate the onset of ulcers.
- Oral Hygiene: Maintaining good oral health through regular brushing and flossing helps prevent ulcer development.
- Avoid Irritants: Steering clear of spicy or hot foods and drinks can reduce the likelihood of ulcer formation.
Conclusion
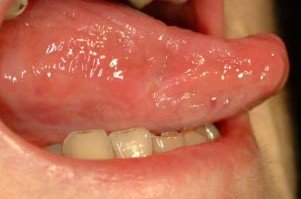
While typically benign and self-limiting, aphthous ulcers can cause significant discomfort. Adopting preventive measures and managing symptoms effectively can enhance comfort and potentially reduce the frequency of these ulcer episodes. For recurrent or severe cases, it is advisable to seek medical advice for tailored treatments and management strategies.